Resource Server
Chapter 3
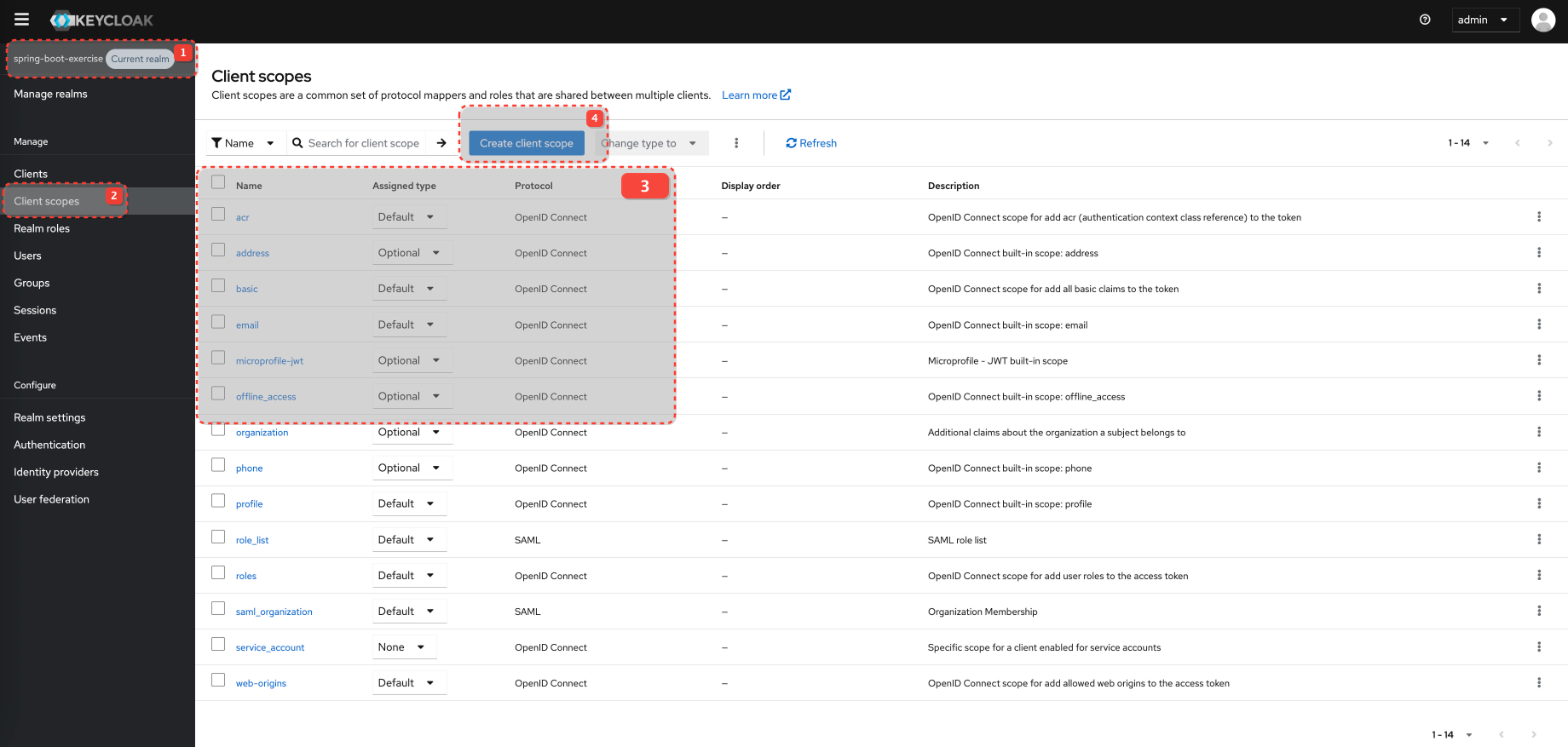
How to define custom client scopes in Keycloak
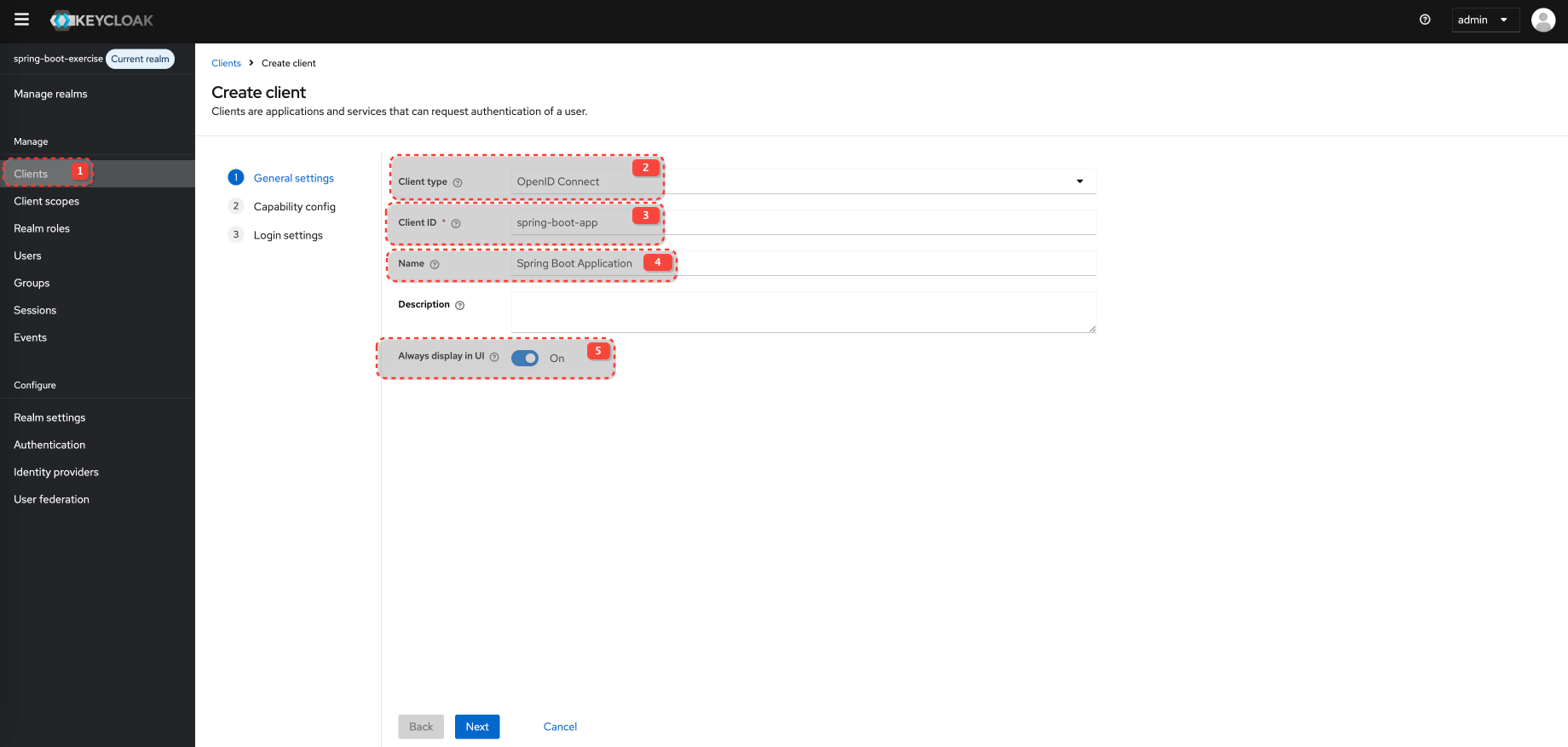
Create new Realm spring-boot-exercise
Realm config details: Realm
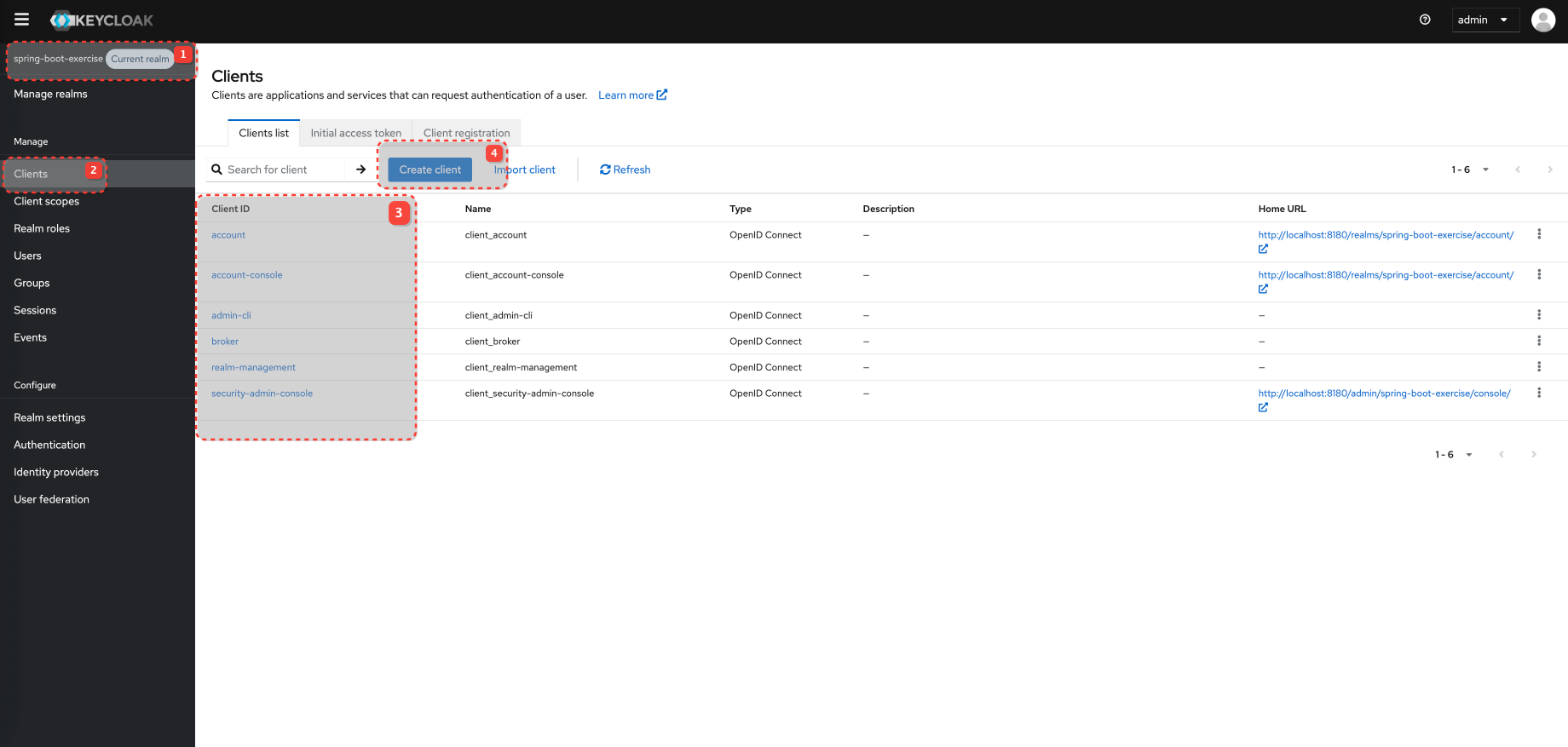
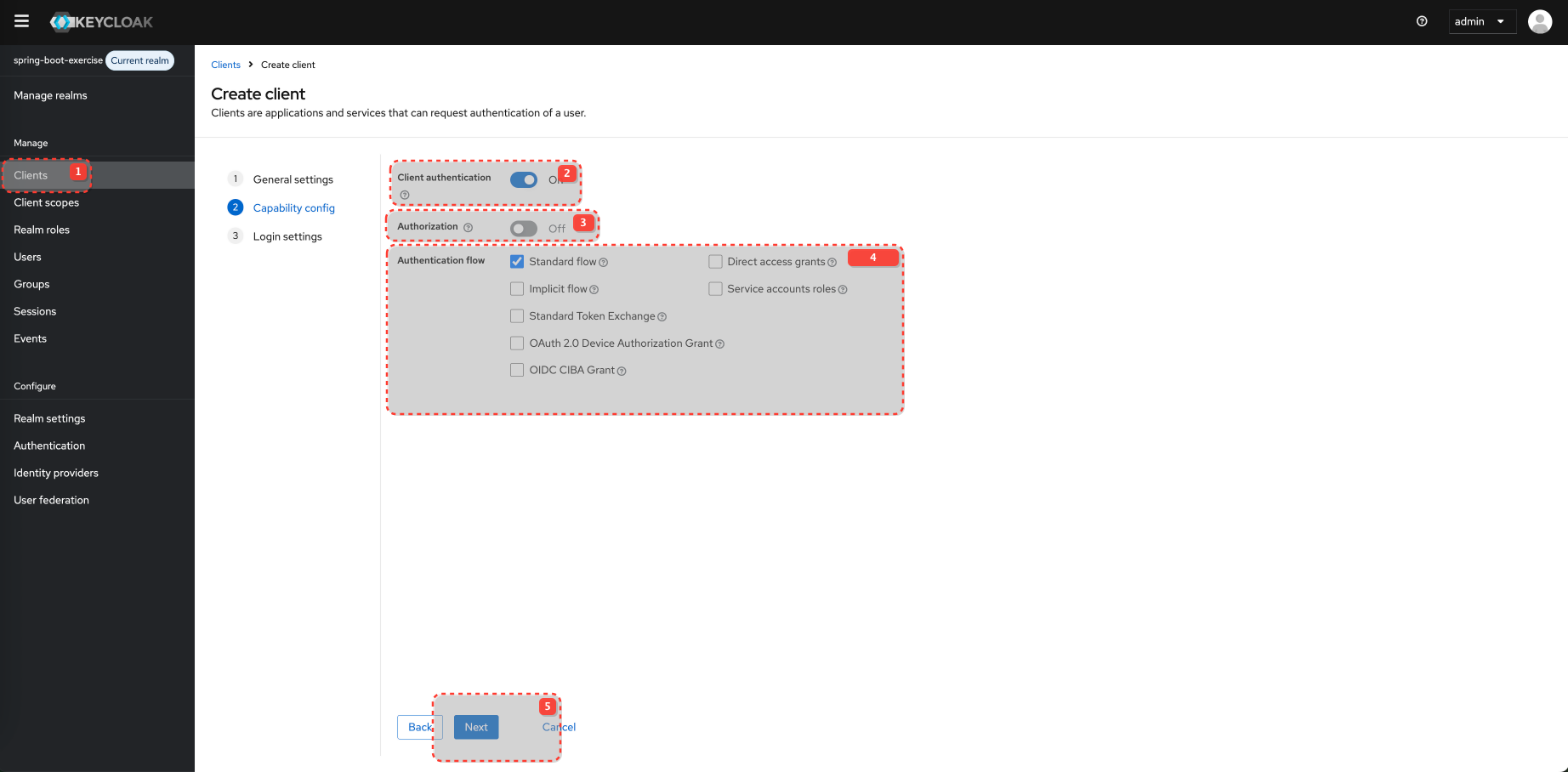
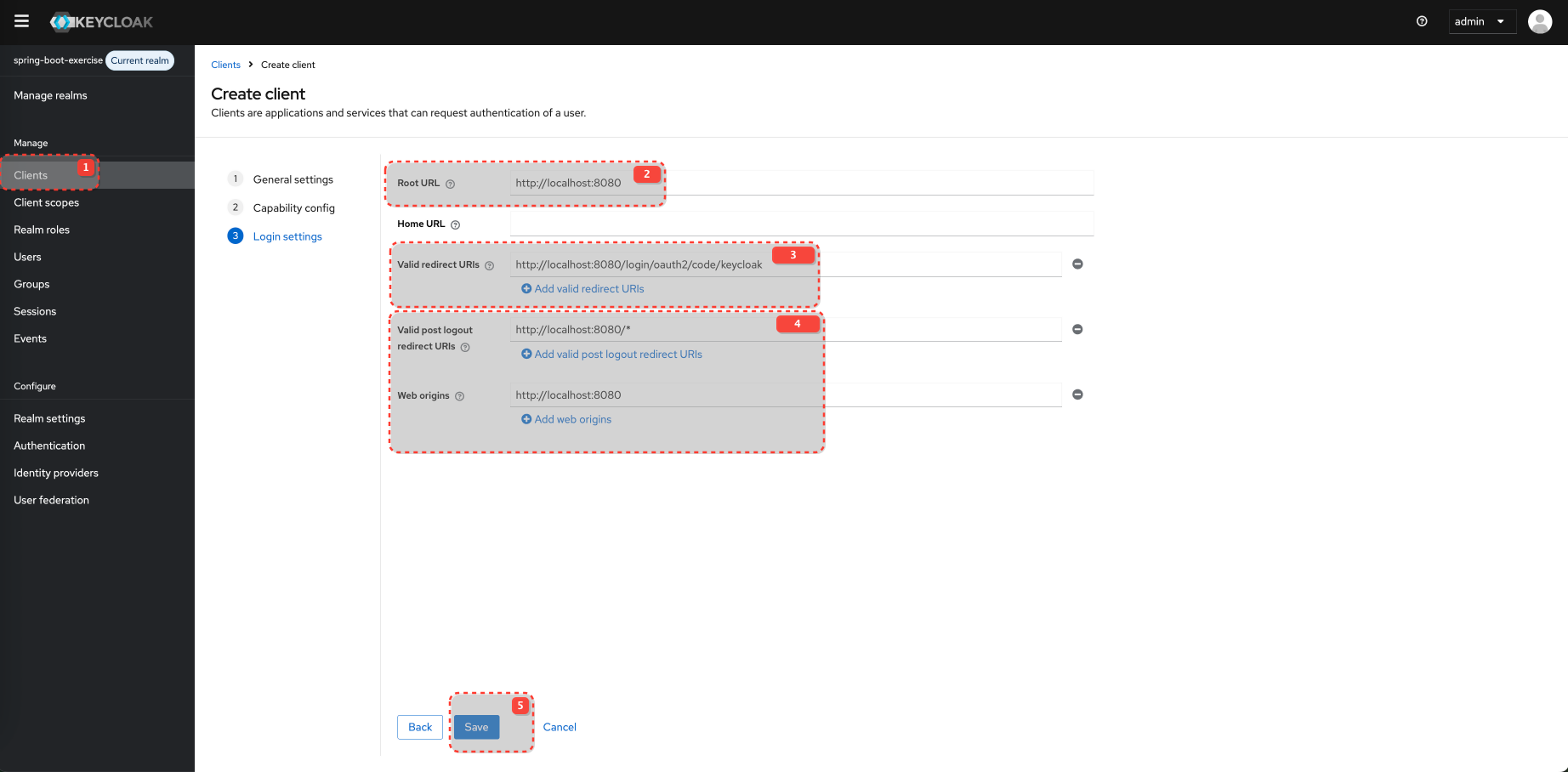
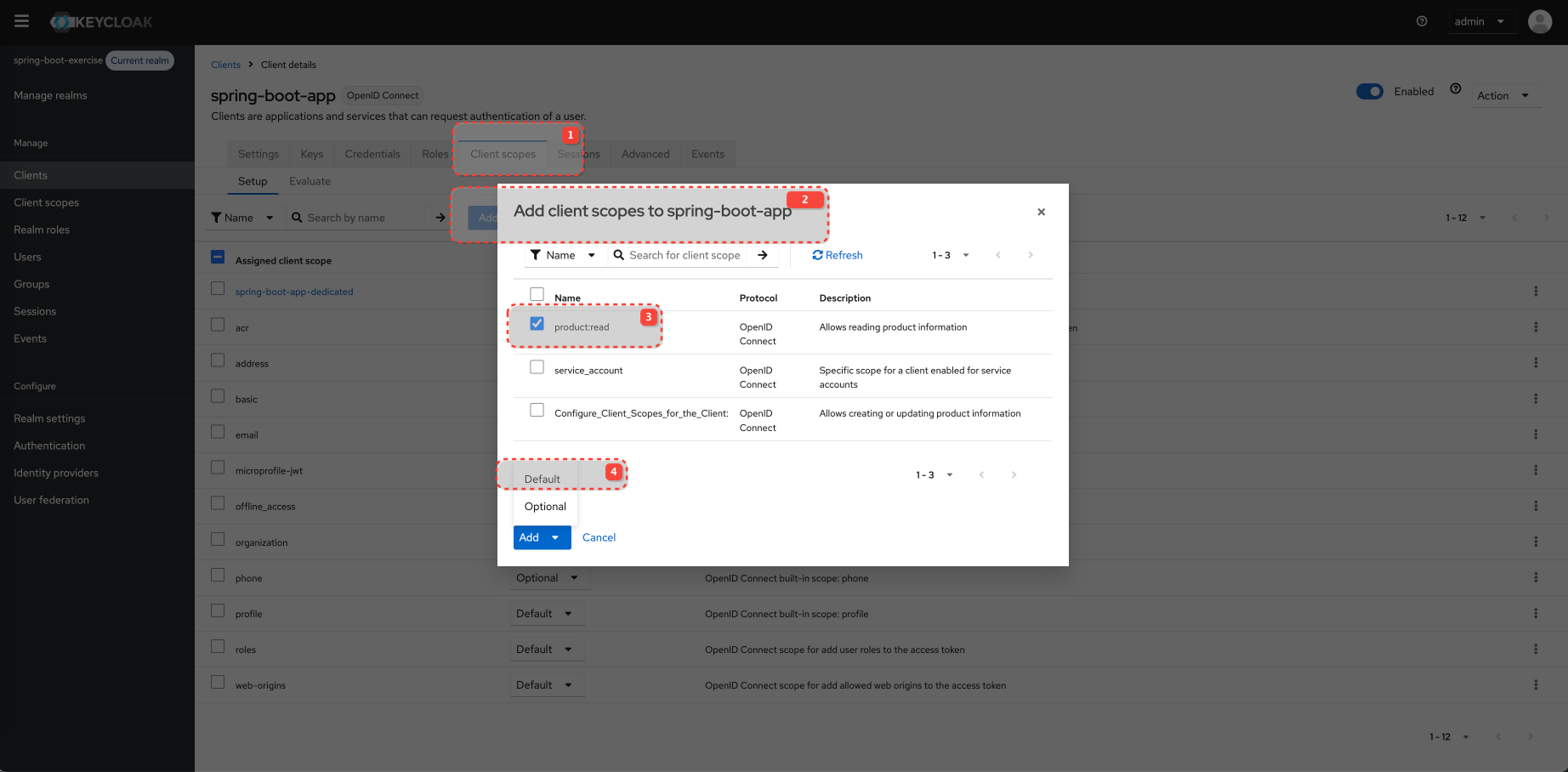
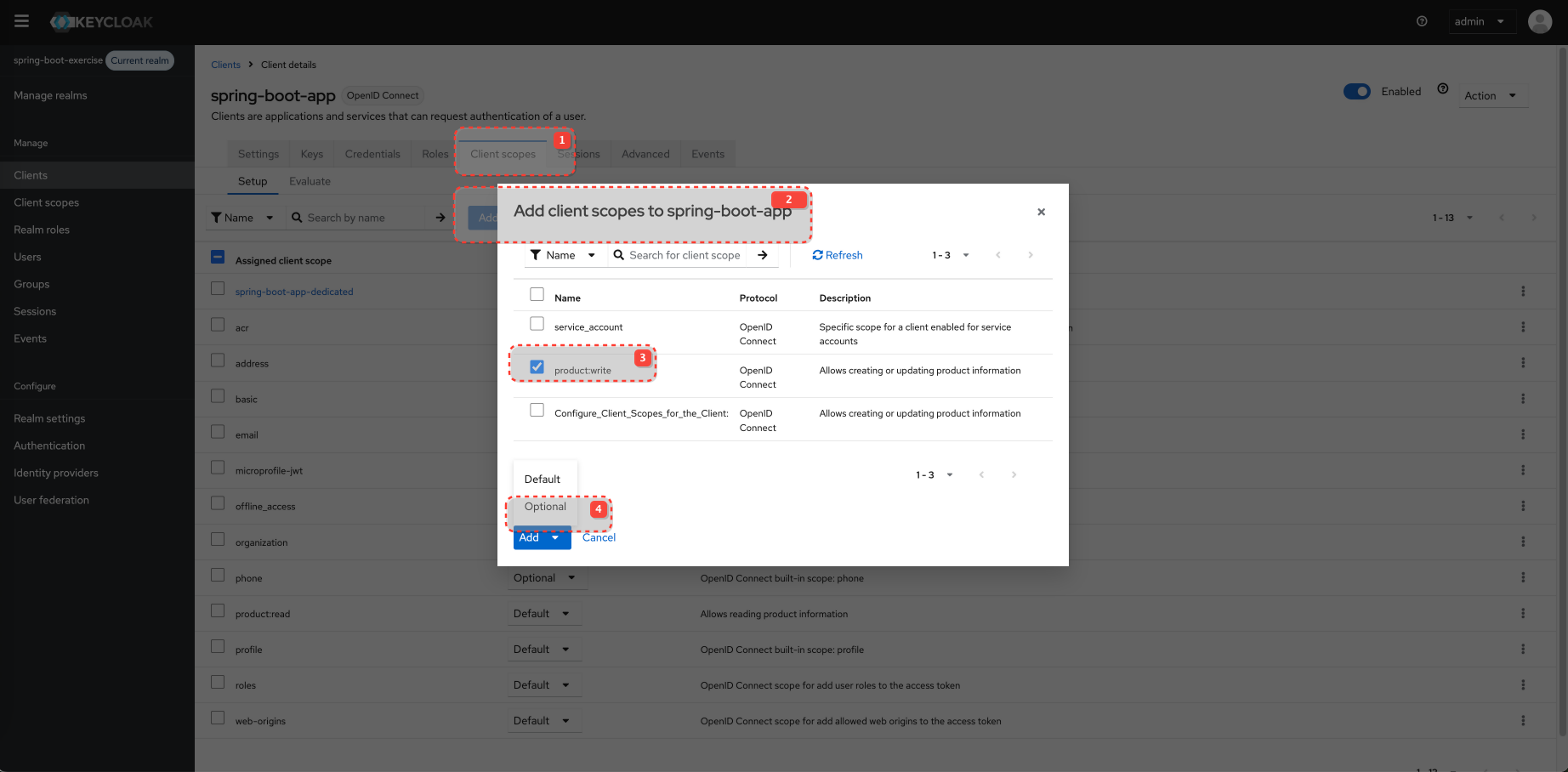
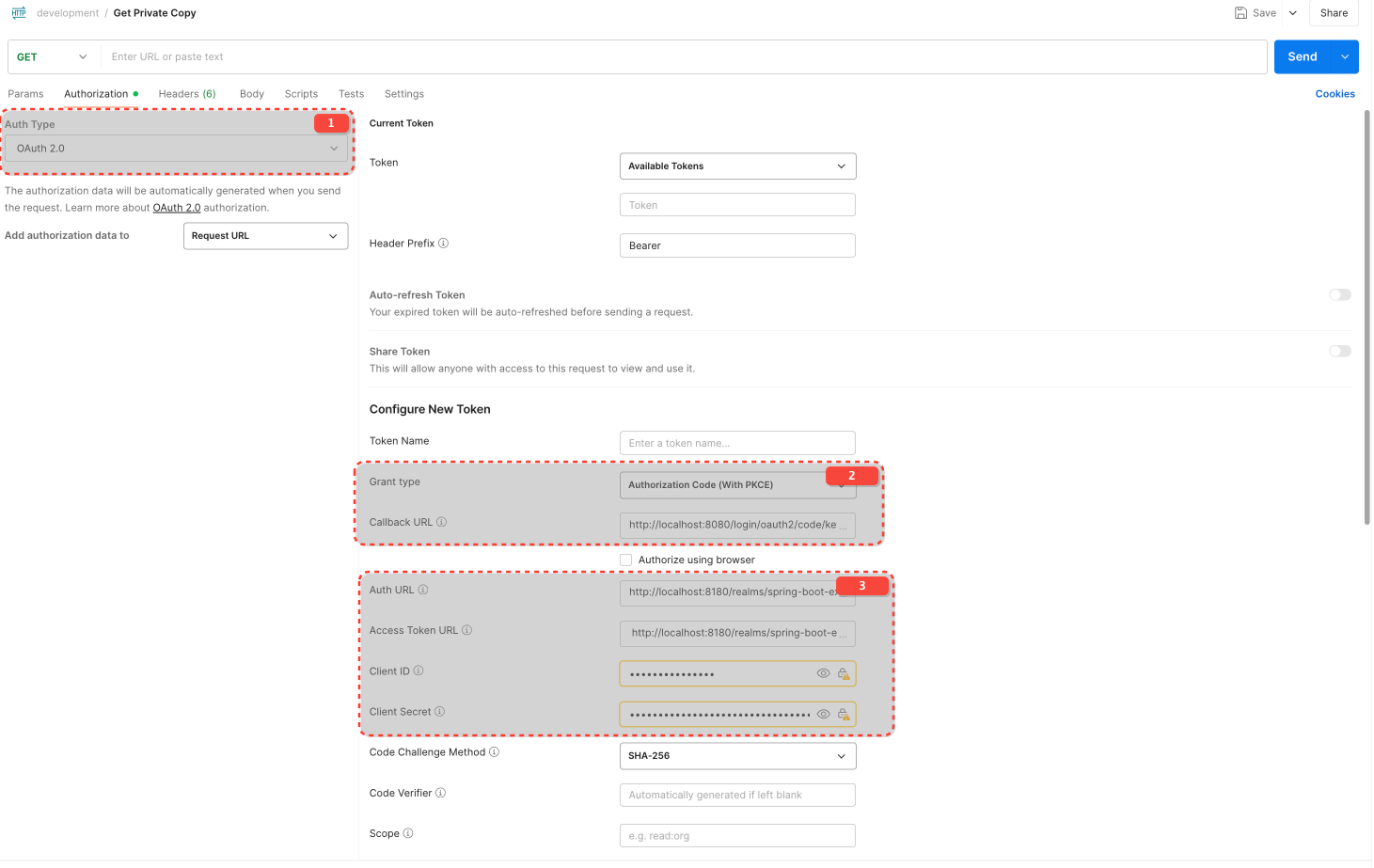
Configure Client and Client Scopes
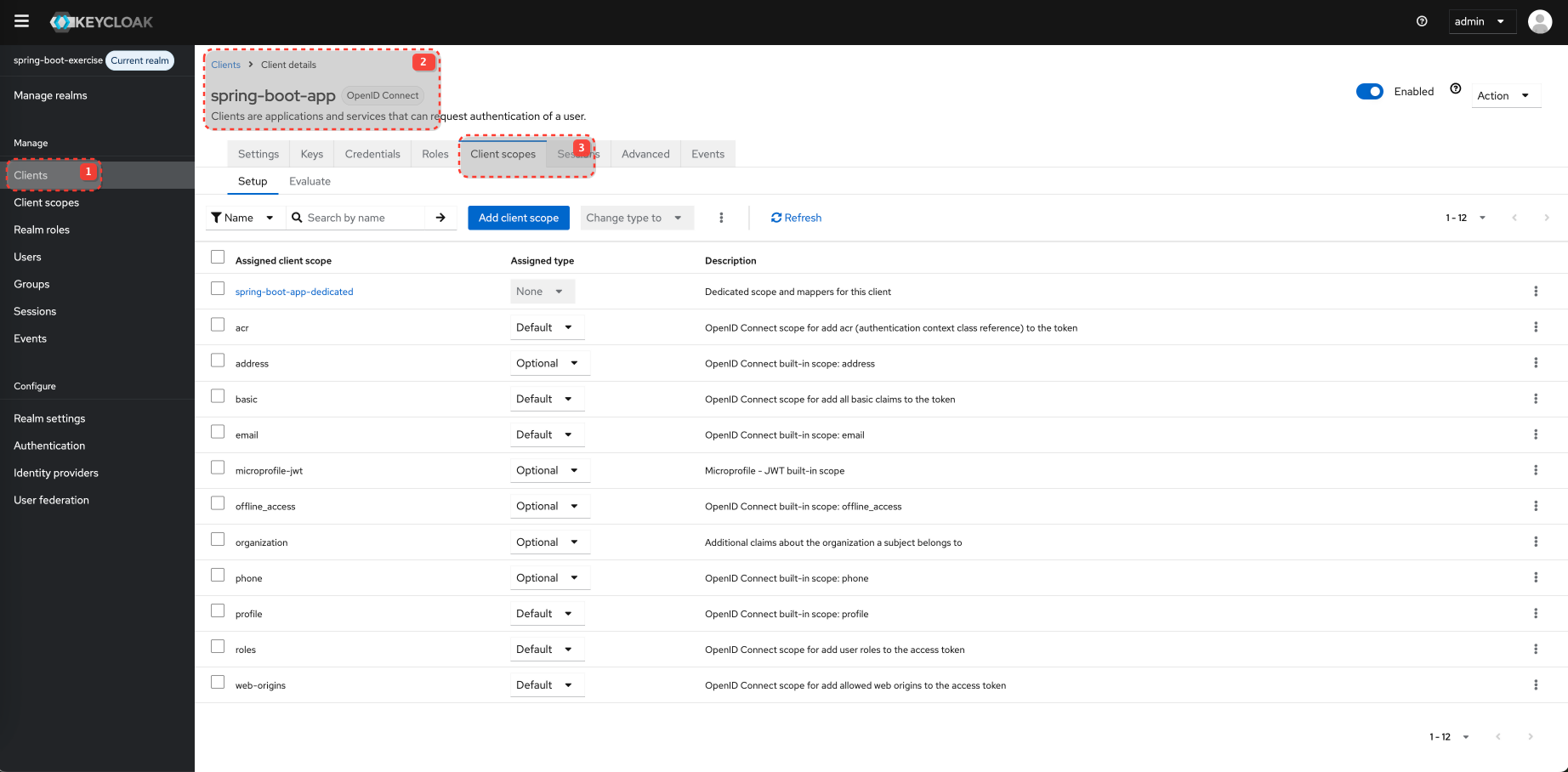
Configure Client Scopes for the Client
Spring Security
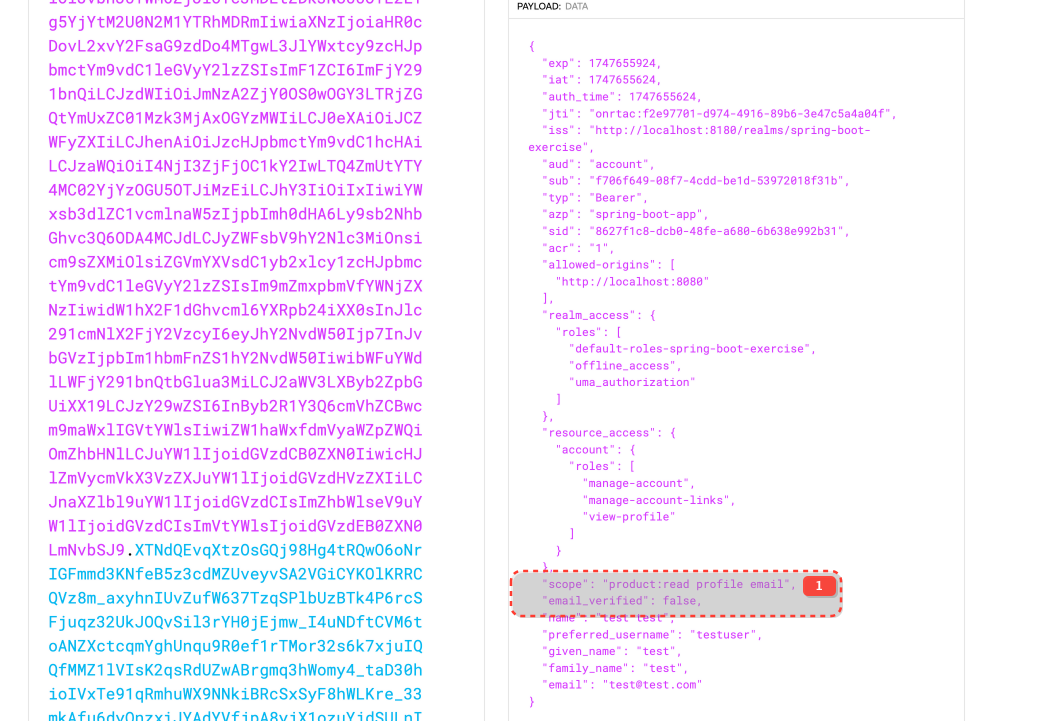
Loading...It looks for the realm_access.roles claim and scope claim (which is a space-separated string).
It prefixes realm roles with ROLE_ and scopes with SCOPE_. This is a common convention for Spring Security.
It also extracts client-specific roles from resource_access.client_id.roles and prefixes them (e.g., ROLE_CLIENT_). You might need to adjust the clientId if it's different or make it configurable.
Application properties
Loading...Controller
Loading...Testing
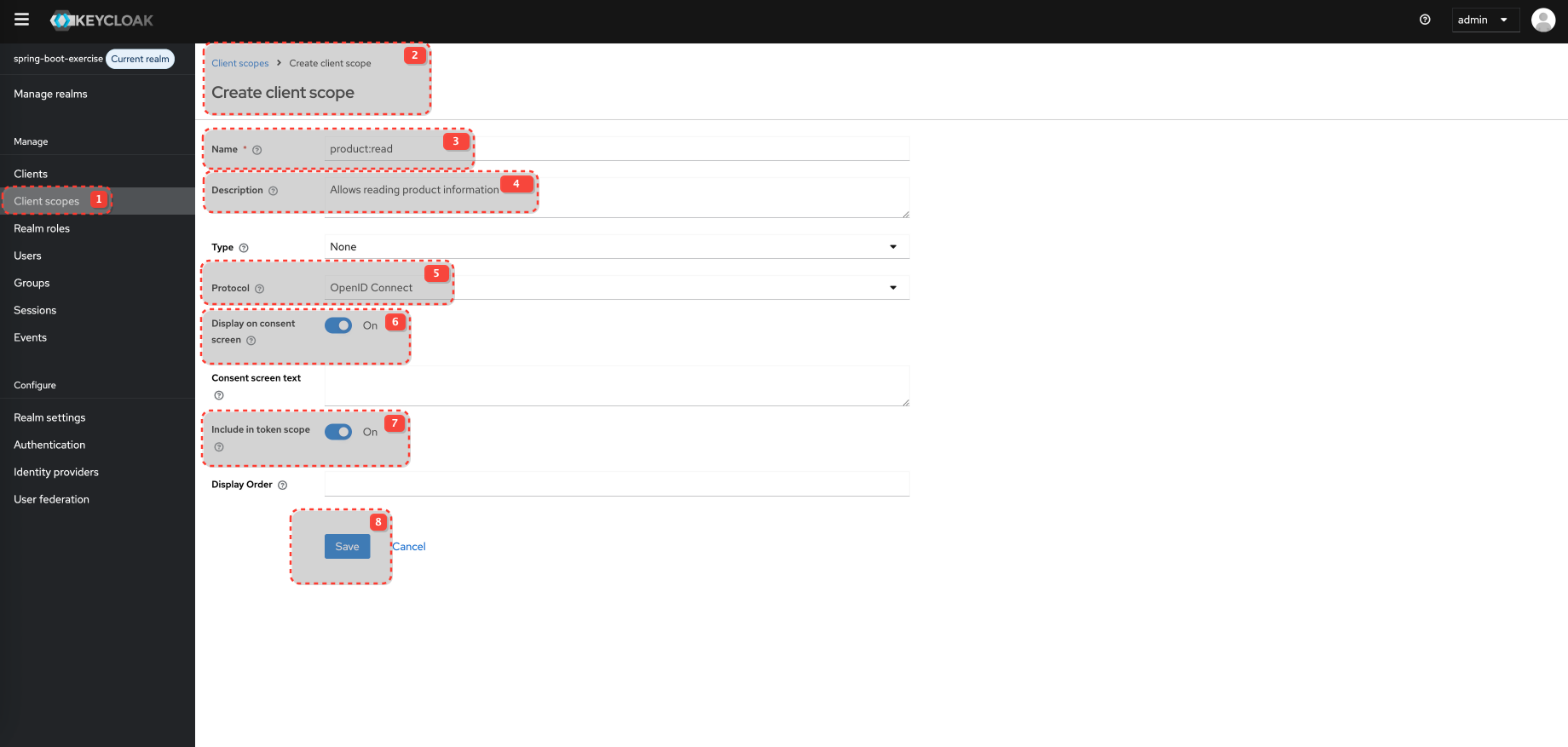
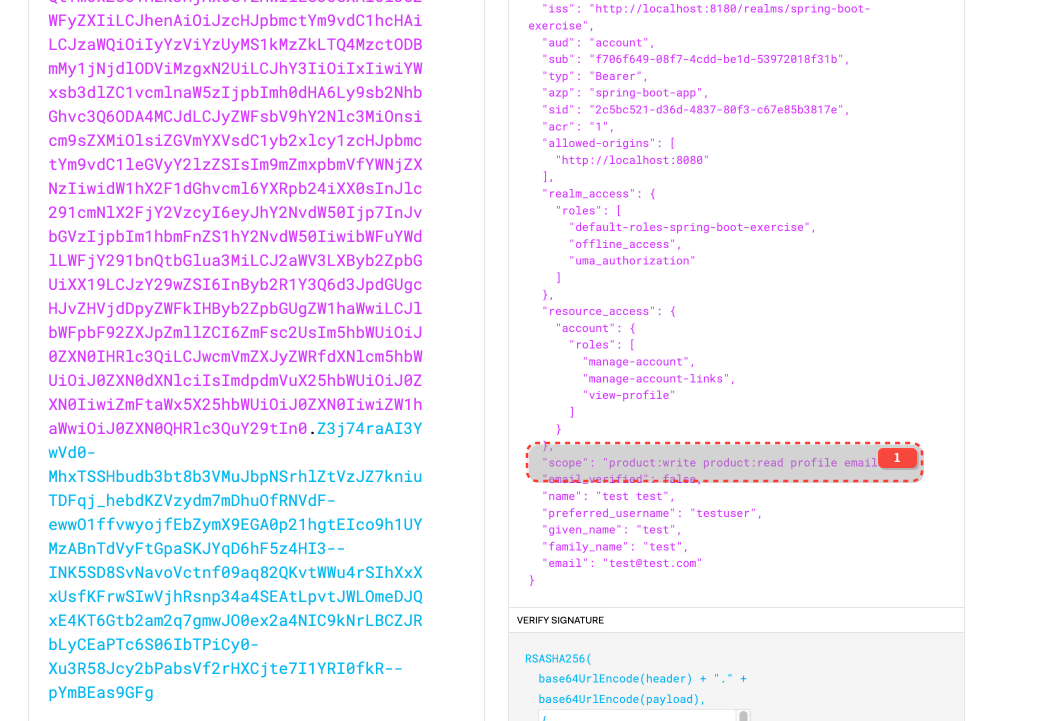
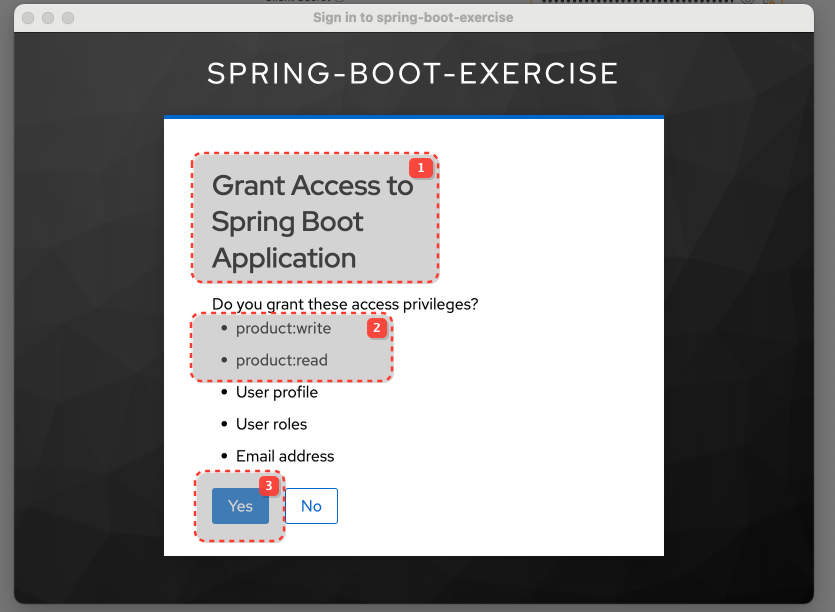
product:read is a "Default client scope" for spring-boot-app in Keycloak and will be added to the token automatically.
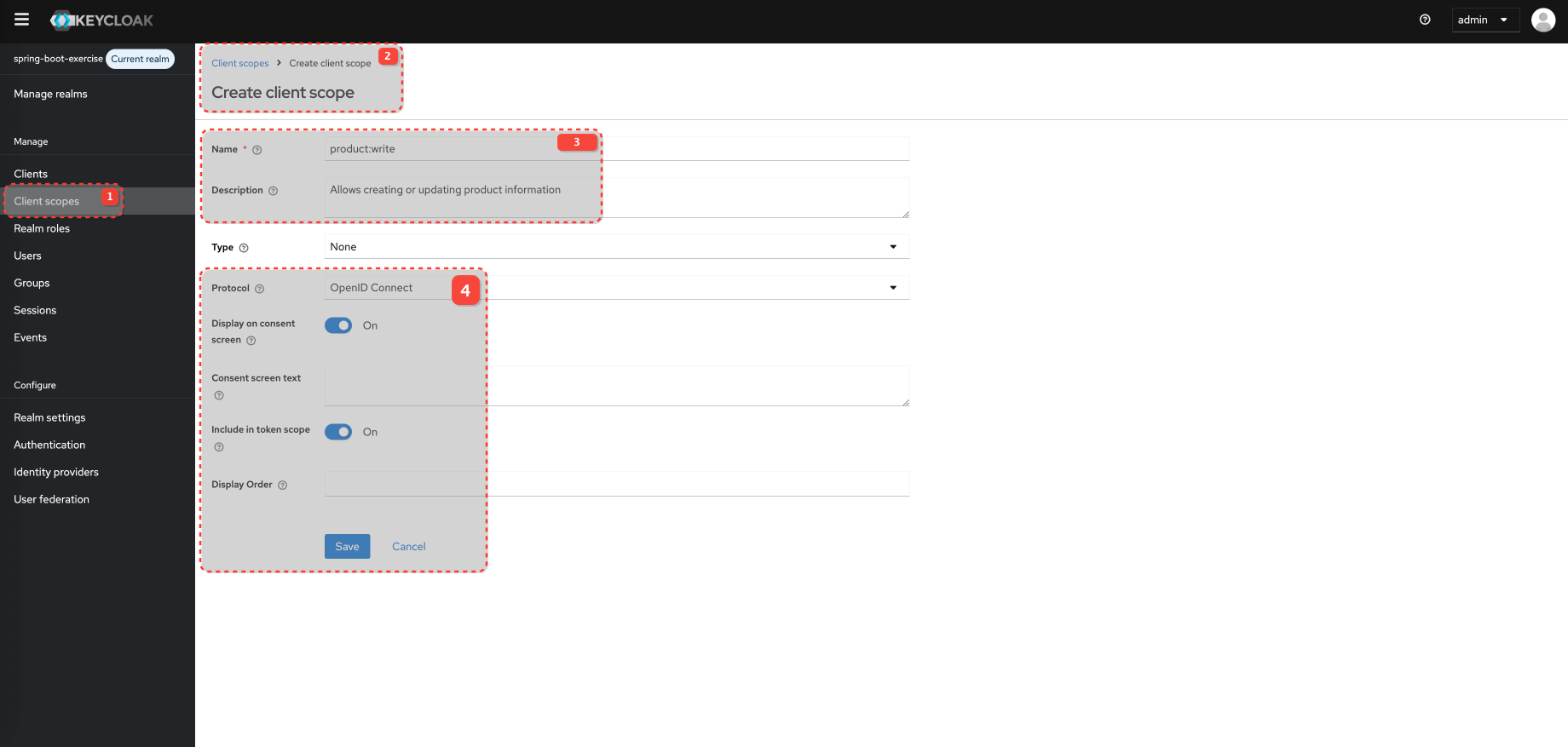
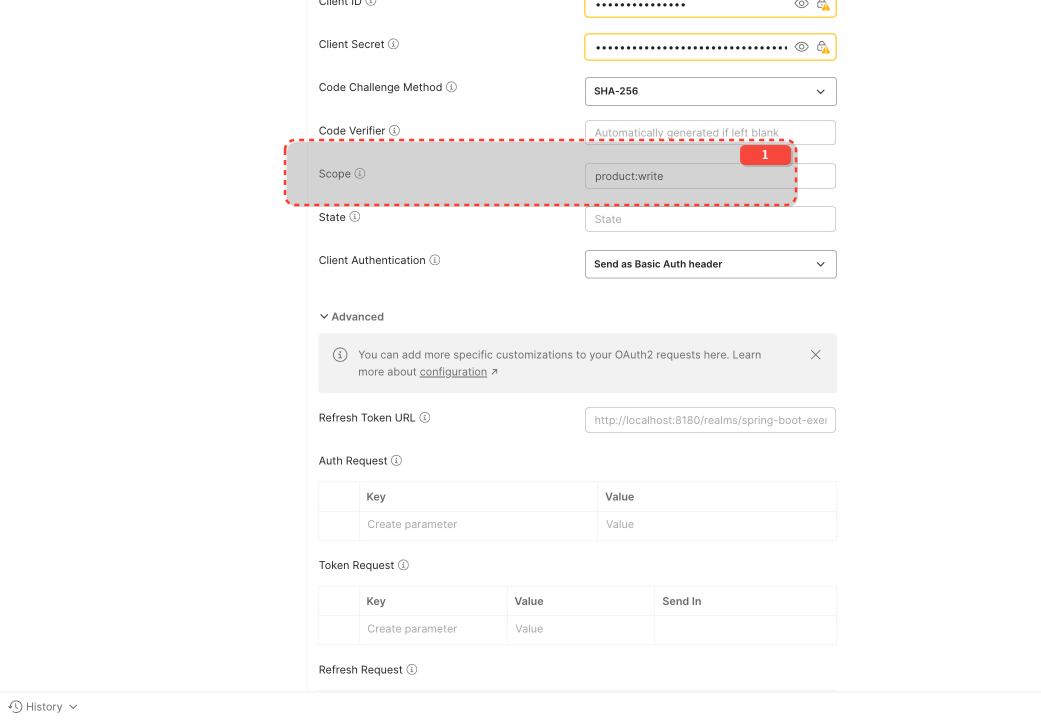
product:write must be requested explicitly.
Default Client Scopes: These scopes are always included in the access token issued for this client, regardless of whether the client explicitly requests them in the /auth request's scope parameter. However, they are still subject to user consent if consent is required. openid is typically a mandatory default.
Optional Client Scopes: These scopes are only included in the access token if the client explicitly requests them using the scope parameter during the authorization flow AND the user consents (if consent is required).
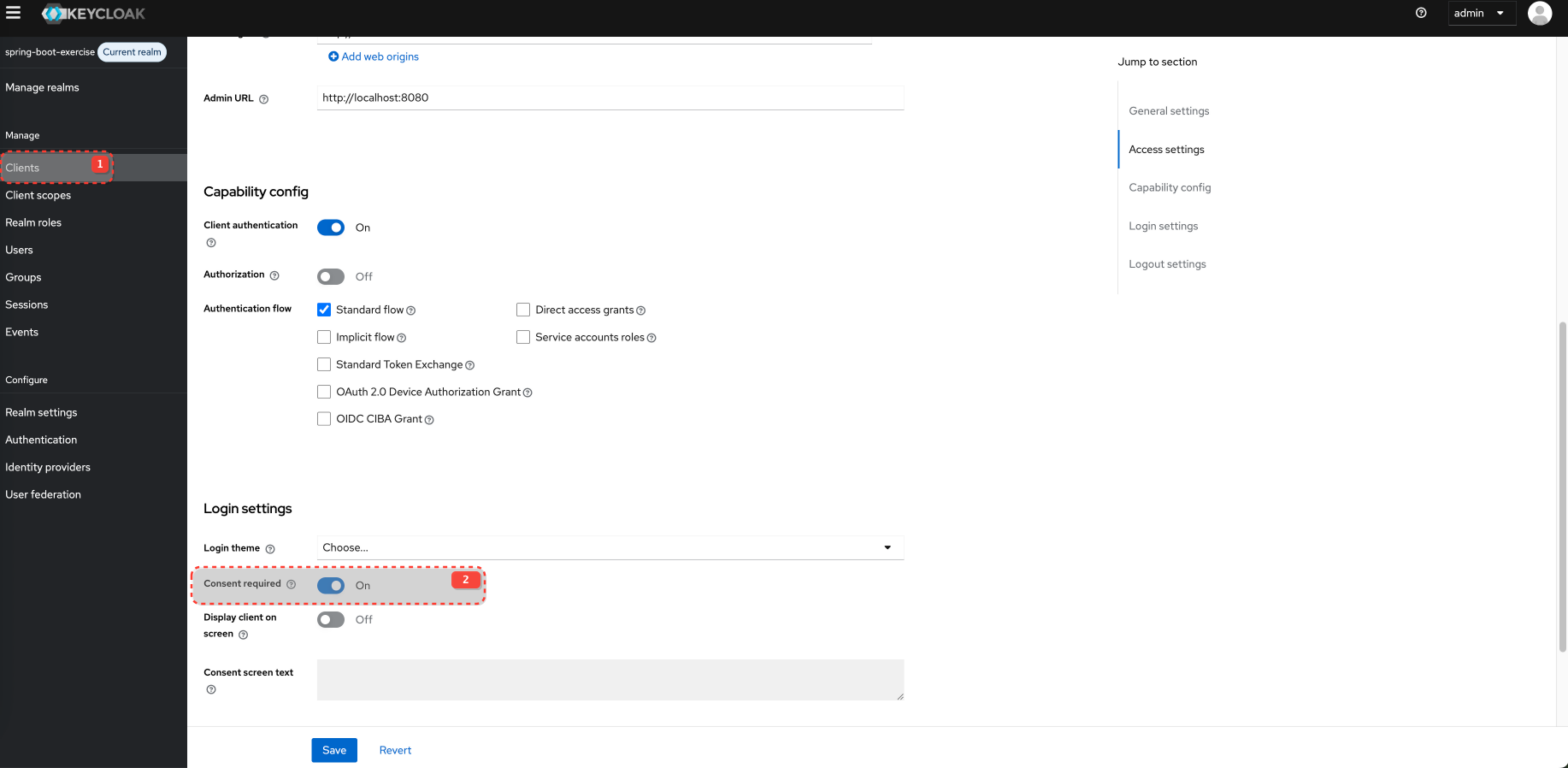
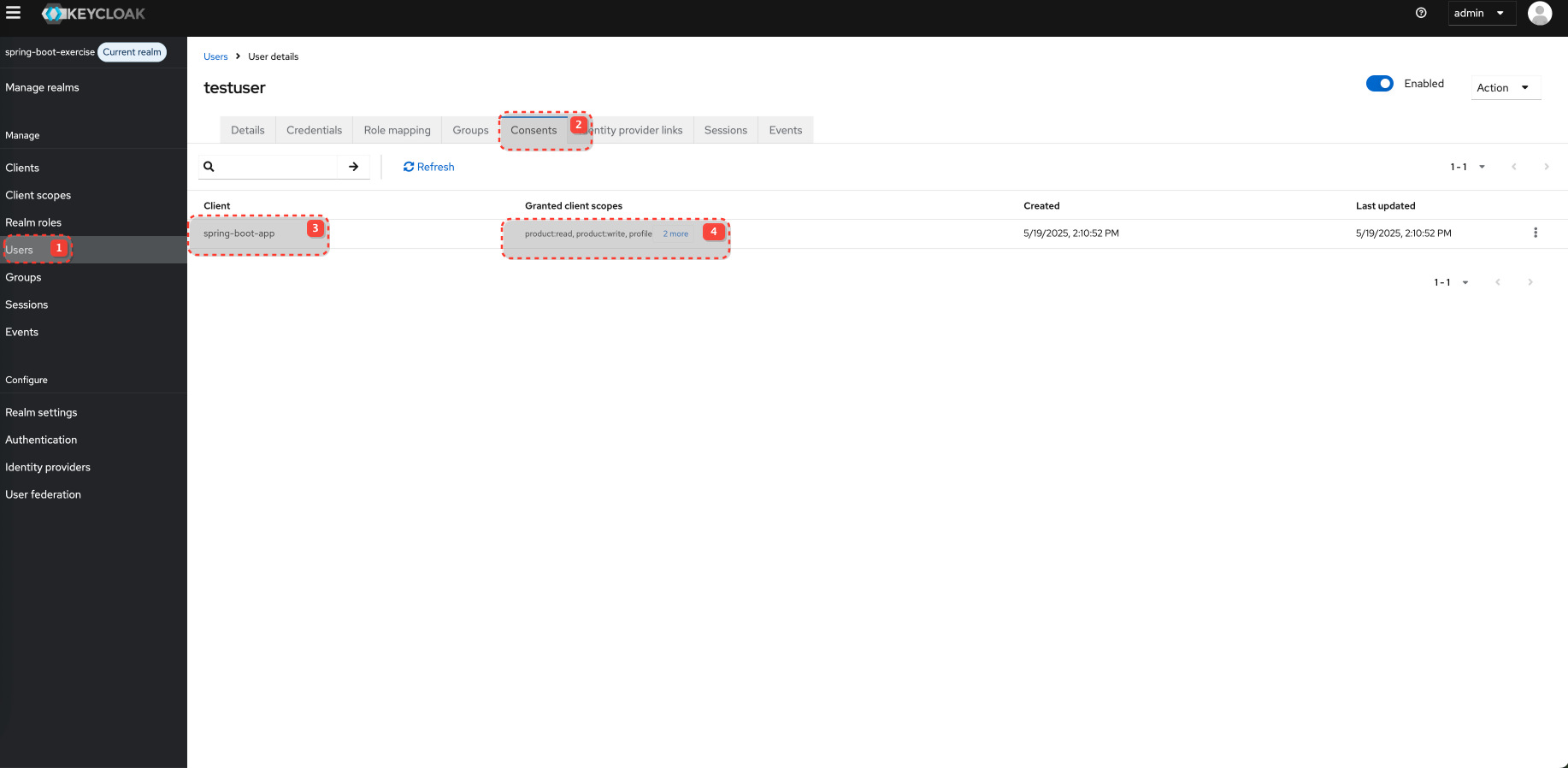
Consent screen
Consent screen is disabled by defualt in client setting for Login UI. You must enable it. Also, when you accept is once, consent is remembered and not shown on next login attempt.
What are client scope mappers and scopes?
Mappers (within a Client Scope):
Focus: Adding data claims (user attributes, properties, hardcoded values) to tokens.
"What information about the user should be in the token if this scope is granted?"
Example: The profile scope uses mappers to add given_name, family_name, etc.
Scope Tab (within a Client Scope):
Focus: Associating permission constructs (Realm Roles, Client Roles) with the client scope.
"If this client scope is granted, what roles should also be considered granted to the user for the purpose of token claims?"
Example: A custom scope document-editor might have the realm role editor assigned to it via its "Scope" tab.
Example, lets say we have 3 roles in system
article-reader
article-writer
article-publisher
You can create client scope: editor-privileges and assign scope (roles)
article-writer
article-publisher
Your cms-frontend now wants to perform an action that requires editing and publishing. Instead of requesting individual roles, it requests the editor-privileges scope: scope=openid profile email editor-privilege